| ||||
The human body is composed of 100,000 billion cells. Whenever a cell divides, its DNA (genetic blueprint) must first be copied, so that each new cell has a complete set of genetic instructions.
Article Summary: A mutation is an alteration of a gene's DNA sequence. Mutations are usually bad news, but those rare changes that benefit an organism are the raw material of evolution.
Role of Genetic Mutation In Evolution
Time-lapse video of cells dividing.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Mutations & Natural Selection
Natural selection is the mechanism of evolution, the process in nature by which the organisms that are best adapted to their environment tend to survive and transmit their genetic characteristics to the next generation in greater numbers. Individuals less well adapted to their environment tend to be eliminated, where environment represents the combined biological and physical influences.
Page last updated: 11/2015
You have FREE access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory biology course. The Virtual Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions & Practice Test Questions.
Relationship Between
Genetic Mutation & Evolution
 | ||||||
The cellular process of copying DNA, replication, is full of mechanisms that carefully proofread the construction of a new DNA molecule. But sometimes mistakes happen when the new DNA molecule is built, mutations (mistakes in the DNA) do occur, and those mistakes are usually harmful, while some have no effect on the organism.
The meaningful differences between organisms in a population are genetic. Variations in the genome of members of a population arise through mutation.
Occasionally, a mutation occurs in an individual that is beneficial, that helps that organism be better able to survive and repoduce in its current environment.
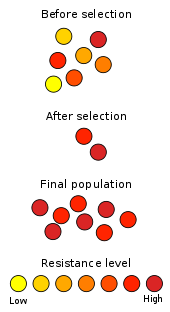
Antibiotic resistance in microbes happens when a microbial population with genetic variation is selected against (killed) through the use of an antibiotic.
Any variant that is resistant to the antibiotic will survive and reproduce. Whereas, microbes without that resistance gene are eliminated. Over time this leads to microbes that are increasingly difficult to kill.
The Power of Natural Selection Over Time
Over time, natural selection can even result in sub-populations within a species being so genetically different that they are no longer able to reproduce with each other. They become separate species (reproductive isolation).
But natural selection does not always result in new forms or species. Natural selection may also result in the elimination of species from the environment
(extinction).
Polar bears (Ursus maritimus) and grizzly bears (Ursus arctos) can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. However, the paths of these two species rarely cross, so breeding between them is rare. The fact that fertile hybrids do occasionally occur, indicates that these two species have more recently diverged.
Mules are sterile hybrids of horses and donkeys, two separate species with interspecific (between species) sterility.