| ||||
MOA of Tetracycline Antibiotics - P2
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
Sources & Resources
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Park Talaro, K (2008) Foundations in Microbiology, McGraw Hill.
- Bayarski, Yuri, "Antibiotics and Their Types, Uses and Side Effects".
- Microbiology In the Home: Tips To Sanitize Your House and Keep Your Family Healthy, Household Microbiology article from Science Prof Online.
- Microbial Control Laboratory Exercise Main Page from the Virtual Microbiology Classroom.
Type of Infections Tetracyclines Are Used Against
Tetracycline is used to treat many different infections including respiratory tract infections caused by Hemophilus influenzae,
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It also is used for urinary tract infections (UTIs), Rocky Mountain spotted fever, typhus, chancroid, cholera, brucellosis, anthrax, syphilis, lyme disease, acne and may be used concomitantly with other medications against Helicobacter pylori, the bacteria associated with stomach ulcers.
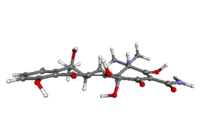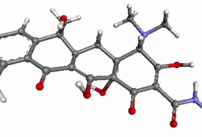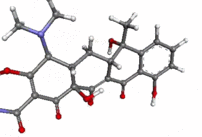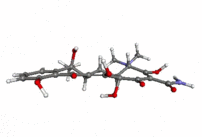
Tetracycline molecule ball-and-stick animation.
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory microbiology course. The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
The SPO website is best viewed in Microsoft Explorer, Google Chrome or Apple Safari.
Page last updated: 8/2015
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
End of Article
Antibiotic Resistance
Because tetracyclines have been around for so long, bacterial resistance is common, and the presence of tetracycline-resistant pathogens limits the use of this class of antibiotic.
Adverse Effects of Tetracyclines
Side effects may include nausea, diarrhea, and sensitivity to light. Tetracyclines also form complexes with calcium, which can stain the developing teeth of children and affect the strength and shape of bones.
Since tetracyclines are active against such a wide range of microbes, destruction of normal intestinal flora often occurs, resulting in increased secondary infections.
* The information in this article is not meant to be used for self-diagnosis or treatment of illness. If you are sick, seek help from a trained medical professional, not a computer.