| ||||
What Is Microbiology?
The Study of Microscopic Organisms
from Science Prof Online
science hobbyist, constructed some of the first high power microscopes. His excellent scopes revealed a world of life too small to be seen by the naked eye.
Leeuwenhoek’s discoveries were the beginning of the end for spontaneous generation, the belief that life could magically spring from nonliving matter on a daily basis. Leeuwenhoek’s findings inspired other scientists to investigate how tiny living things seem to appear from nowhere—in rainwater, spoiling food and the human body—and led to the understanding that life springs from life.
This explosion of scientific inquiry into the microscopic world resulted in a dramatic change in medicine called Germ Theory, the knowledge that some diseases were caused by microbes.
What Are Microbes?
Organisms that are typically studied by microbiologists fall into seven basic categories: fungi, protozoa, algae, bacteria, archaea and viruses.
FUNGI: These eukaryotic organisms can be quite large, like the underground fungi that generate mushrooms, or they can be very small, such as tiny molds and yeasts. As important decomposers of dead organisms, fungi are essential to recycling matter in living systems. But there are also fungi that cause disease.
PROTOZOA: Protozoans are single-celled eukaryotes that have animal-like characteristics, in their cell structure as well as how they procure food and move about. Members of this group include amoebae, flagellates, ciliates and sporozoans. Most protozoans live in water, but some live in human hosts and are able to cause disease.
ALGAE: These water-loving eukaryotes can range in size from microscopic, single-celled organisms to giant kelp. Algae are more plant-like than animal-like, in that they make their own food from carbon and sunlight energy (photosynthesize). Most algae are beneficial, even critical for life on earth. Few cause disease.
BACTERIA: Bacteria are single-celled prokaryotic organisms. They have cell walls made of peptidoglycan, a molecule not found anywhere else in nature. Bacteria are all around us. Some are normal flora that naturally inhabit the human body and are helpful or at least not harmful. Bacteria are also utilized to make enzymes for detergent and antibiotics against other types of bacteria. But there are also many bacterial pathogens that cause disease.
ARCHAEA: This is a group of prokaryotic microbes is very similar to bacteria. However, their cell walls are not made of peptidoglycan, and there are no known Archaea that cause disease in humans.
VIRUSES: Viruses are acellular, non-living infectious agents. They are smaller than cells and are strictly parasitic. Viruses cannot reproduce on their own. They must first find a cell to infect, which will then function as a factory for making more viruses. Viruses are so small that they cannot be seen with a compound light microscope, the type of scopes typically used in laboratories to see small organisms. These minute microbes can only be seen using a high-tech electron microscope.
Sources & Resources
- Bauman, R. (2014) Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy, 4th ed., Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
- Nester, E. et al (2001) Microbiology: A Human Perspective. McGraw Hill
- Tortora, G., Funke, B., Case, C. (2010) Microbiology, an Introduction. Benjamin Cummings.
- Introduction to Microbiology Lecture Main Page from the Virtual Microbiology Classroom.
Article Summary: Microbiology, the study of microscopic (very small) forms of life, has transformed our understanding of the world. These tiny things are a big deal.
What Is Microbiology?
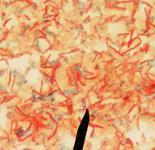
Stain of endospore-producing Bacillus subtilis: Endospores green, vegetative cells red.
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory microbiology course. The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
Page last updated: 10/2014
SCIENCE PHOTOS
 | ||||||
SPO is a FREE science education website. Donations are key in helping us provide this resource with fewer ads.
Please help!
(This donation link uses PayPal on a secure connection.)
SPO VIDEO Tutorial on Compound Light Microscope Parts & Operation
Throughout most of history, people had no knowledge of the minute organisms that exist everywhere, and the implications of this ignorance were huge. Infectious disease could not be understood, prevented or cured, prior to the discovery of microorganisms. Modern infectious disease medicine is built upon a solid understanding of microbiology.
Early Pioneers of Microbiology
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch merchant and
 | ||||||
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||