| ||||
Bacterial Colony Morphology & Bacterial ID - P2
Page last updated: 3/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
Continued >
Bacillus subtilis
colonies
Adjectives Used to Describe Bacterial
Colony Morphology
The Bacillus subtilis colonies in the photo to the left are
motile. They have flagella which allow them to move. So the descendants expand out from their parent bacteria, resulting in large colonies with wavy, lobed margins.
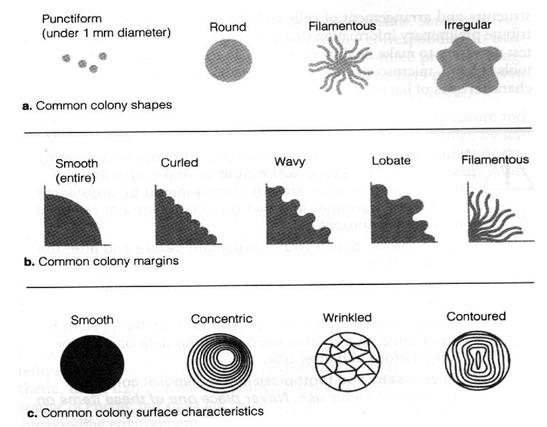
The illustration below, provides some basic terms that are helpful in documenting colony morphology.
Describing Bacterial Colony Morphology
Although bacterial colonies can differ in the details of their appearance, a colony basically looks like a dot growing on the medium. This dot is composed of millions of bacteria that arose through binary fission from one initial bacterium, the parent.
Description of a colony's morphology includes its shape, the margins or edges of the colony, its color, and surface features. Some colonies are round and smooth, others can have wavy edges and a wrinkled appearance.
There are an amazing variety of bacterial colony types.
The morphology of a colony results from characteristics of the individual bacteria viewed collectively.
For example,
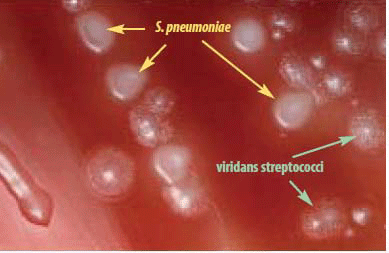
Streptococcus pneumoniae colonies are smooth in appearance if the bacteria have a protective glycocalyx capsule and the colonies appear rough appearing in strains that do not have capsules.
 | ||||||
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in two college-level introductory microbiology courses (8-week & 16-week). The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.