| ||||
What Is RNA and What Does It Do? - P2
Page last updated: 2/2016
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a high school / college-level introductory biology course. The Virtual Biology Classroom is new and, as it is developed, a wide range of free educational resources will be added, including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
What Does RNA Do?
RNA is involved in gene expression; the process of building a protein molecule coded for by a gene. Gene expression involves RNA in two processes:
transcription and
translation.
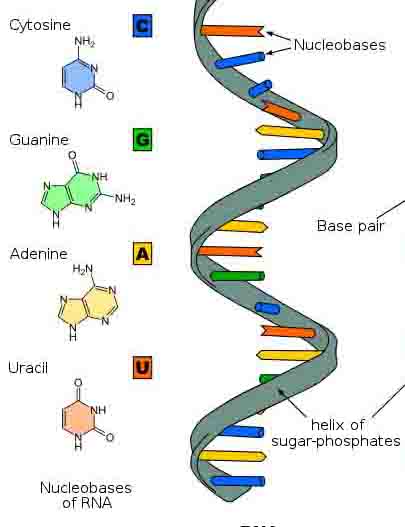
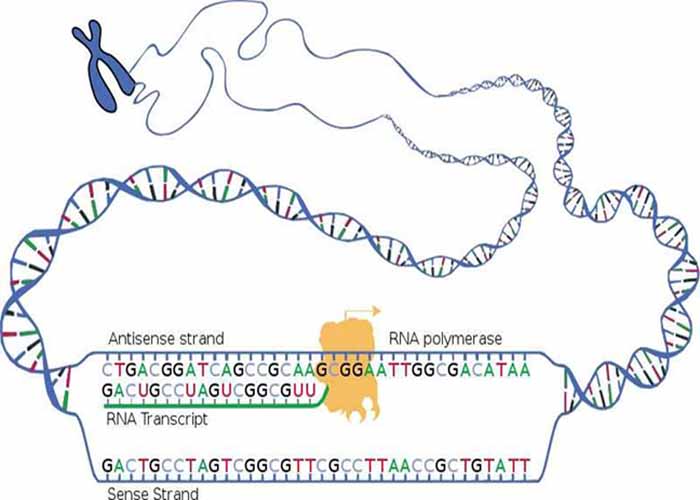
Genetic Transcription: This is the process by which a DNA sequence is copied to produce a complementary RNA segment. In other words, it is the transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA; like DNA replication, but the nucleic acid RNA is made instead.
DNA is the only original copy of the genetic instructions that a cell has. Rather than use this original to direct the building of proteins, mRNA copies of the information are made that can travel to the ribosome to direct protein synthesis.
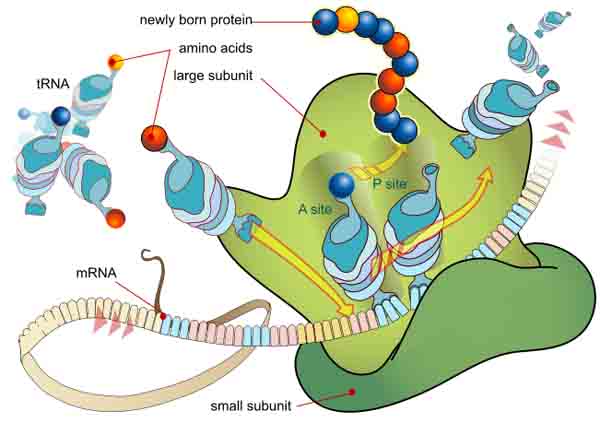
Genetic Translation: Making proteins from instructions contained in the genetic code is called translation. The mRNA goes to a ribosome, where it is read in three nucleotide sections called codons. Each codon calls for a tRNA to bring a specific amino acid. This is the Genetic Code. Once the entire mRNA molecule is translated, numerous amino acids have been brought to the ribosome and joined together to form a strand of protein.
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
Genetic Transcription: This is the process by which a DNA sequence is copied to produce a complementary RNA. Rather than use this original to direct the building of proteins, mRNA copies of the information are made that can travel to the ribosome to direct protein synthesis.
Genetic Translation:
Making proteins at the ribosome, from instructions contained in the genetic code. Transfer RNA (tRNA) are the "trucks" that bring the amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
To learn more about molecular genetics see the following animations and SPO Class Note Articles:
Animations
- DNA Structure Cell Biology Animation from John Kyrk.
- DNA Transcription step-through animation by John Kyrk.
- DNA Transcription and Protein Assembly animated movie by RedAndBrownPaperBag.
- Transcription & Translation animated movie, PBS production “DNA: The Secret of Life."
Student Resources & Assignments
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid Structure – What Is DNA?
- Genetic Replication – Copying of DNA
- What Are Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids? Structure and Function of DNA, RNA and ATP
- Nucleic Acid Function of DNA & RNA: Genetic Replication, Transcription & Translation
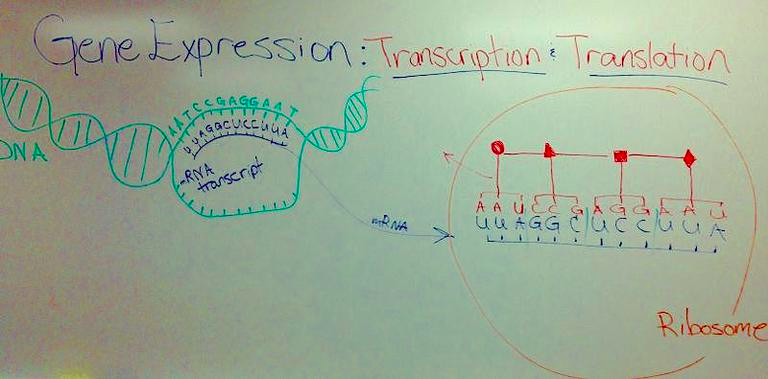
Gene Expression Diagram Showing
Transcription & Translation
You have free access to a large collection of materials used in a college-level introductory Cell Biology Course. The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
VIDEO
on
Genetic Transcription & Translation
from
Crash Course Biology