| ||||
Differential Stains for Identifying Bacteria
Gram, Acid-fast & Endospore
The Gram stain, acid-fast stain and endospore stain each reveal distinct information about the bacteria tested.
What the Gram Stain Reveals about Bacteria
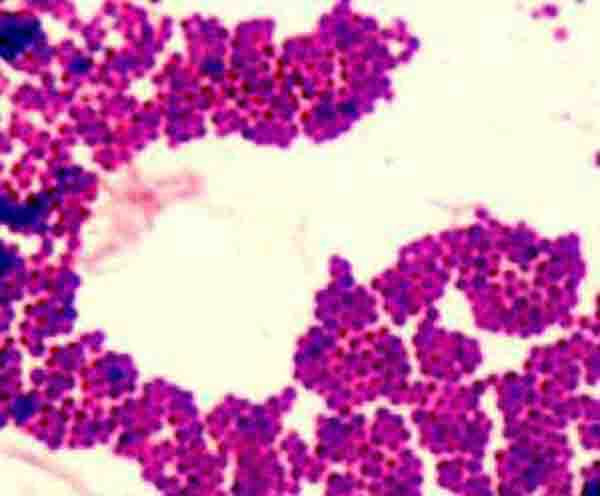
The Gram stain, developed by Christian Gram in the 1800’s, was the first differential staining technique in use and is still an important tool for distinguishing between two main types of bacteria—Gram-positive and Gram-negative.
Article Summary: The Gram, Ziehl Neelsen acid fast, and endospore stains are differential tests used to help identify bacteria. Here's how they work.
Gram, Acid-fast & Endospore Bacterial Stains
Page last updated 3/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
SCIENCE VIDEOS
Differential stains work by using a series of dyes, and sometimes additional chemicals, to stain bacteria in contrasting colors based on structural difference between bacterial cells.
After rinsing, a decolorizer is applied that removes the purple stain from Gram-negative cells, leaving them colorless. After rinsing the decolorizer, a secondary stain (safrinin) is then applied to impart a pink color to the Gram-negative cells.
After a final rinse, the slide can be viewed under oil immersion with a light microscope. Gram+ cells will appear purple and Gram- cells pink.
The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of FREE educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
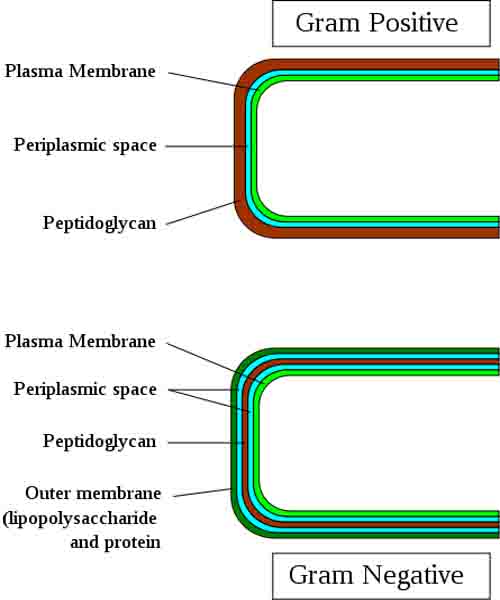
Nearly all bacteria contain peptidoglycan, a molecule unique to the bacterial cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria have a cell wall composed almost entirely of peptidoglycan, present in many layers. Gram-negative bacteria have a cell wall with only a thin layer of
peptidoglycan beneath an outer cell wall membranous layer composed of lipopolysaccharides(LPS), an endotoxin that can be harmful to organisms infected with Gram-negative bacteria.
During the Gram staining technique, a purple dye (crystal violet) is first applied to a prepared bacterial smear. After rinsing, iodine is then applied. The crystal violet and iodine bind to create a large molecule that is too big to exit the multiple layers of peptidoglycan in the Gram positive cells, so the purple color becomes trapped.