| ||||
Plant Cell Parts,
Functions & Diagrams
Everything that is alive is made of one or more cells. The cell is the smallest unit of life, and there are two main types:
- Prokaryotes = bacteria and their bacteria-like cousins Archaea
Article Summary: The cells of plants are eukaryotic, with a nucleus, a vacuole, membrane-bound organelles and a cell wall. Here's a summary of the structure and function of plant cells.
Plant Cell Parts, Functions & Diagrams
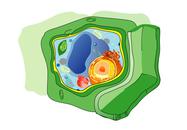
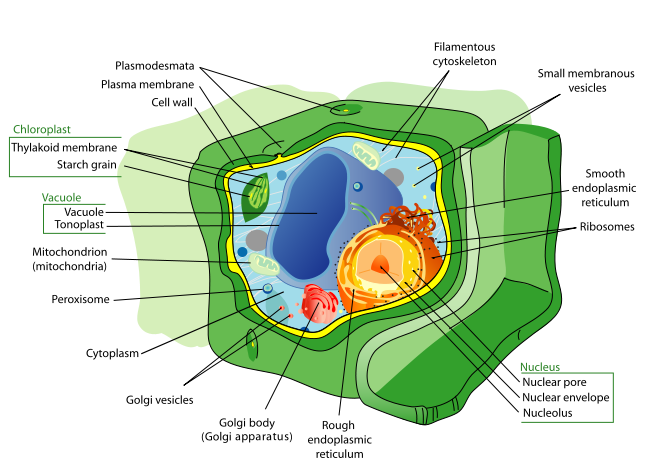
Image of generic plant celll. Click here for a labeled diagram of this cell.
SCIENCE PHOTOS
Page last updated: 1/2016
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
 | ||||||
VIDEO: How to Make a Wet Mount Slide of Elodea Plant Cells
- Eukaryotes = the more complex cells of animals, plants, fungi, protozoans, algae, and slime and water molds
Although eukaryotic cells share many characteristics, there are also specializations that make plant cells unique. The following is a rundown of the main features differentiating plant cells from other eukaryotes.
Structures Present in Plant Cells & Absent in Animal Cells
- Cell wall: Plant cells have protective cell walls, composed mainly of structural carbohydrates. The cell wall provides support, helps maintain cell shape, and prevents the cell from taking on too much water and bursting. The cell wall is not a feature unique to plants; bacteria, fungi and some protists also have cell walls. But unlike the cell walls of bacteria and fungi, plant cell walls are composed of different types of carbbohydrates—cellulose and hemicellulose—and structurally consist of three layers; an outer primary cell wall, a sticky pectin layer called the middle lamella, and a secondary cell wall, closest to the plasma membrane.
The Virtual Cell Biology Classroom provides a wide range of free educational resources including Power Point Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
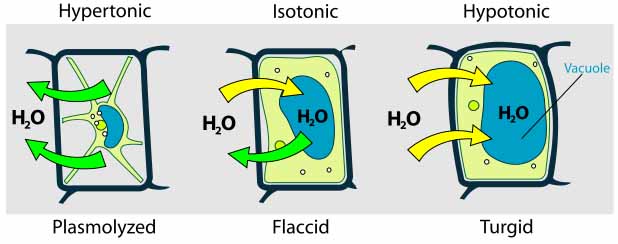
- Central vacuole: The central vacuole takes up most of the space within a plant cell. Defined by a membrane called the tonoplast, the central vacuole functions as a holding tank for water and other molecules used by the cell. When full of water, the vacuole presses the other cell contents against the boundary of the cell.
- Chloroplasts: These double membrane bound organelles contain the green pigment chlorophyll, which captures sunlight energy, so that the cell can produce its own food, a process called photosyntheses. Chloroplasts are just one type of plastid organelle common to plant cells. Some plastids function in food storage; others house different types of pigments that impart colors other than green to plants.
Turgor pressure or turgidity is the pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall, in plant cells, determined by the water content of the vacuole, resulting from osmotic pressure.